A pattern that happens all too often in motor vehicle accidents is that an injured person will complain of headaches, dizziness, nausea, or other symptoms of a mild traumatic brain injury (TBI), all while the medical scans appear normal.
In the aftermath of an accident, emergency room doctors order imaging studies – either a CT-scan (computerized tomography) of the person’s head or an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging). Often, those imaging studies come back “normal,” showing no acute signs of an injury to the brain, even while the injured person experiences problems long after the accident. On occasion, the symptoms can worsen over time. Why do the CT-scans and MRIs come back showing no injuries?
What is a CT scan?
A CT scan is an advanced form of x-ray technology that uses computer processing to create a more detailed picture, versus a standard x-ray. CT scans are routinely performed today in the emergency department to look for acute fractures, cranial hemorrhaging, swelling, or other life-threatening conditions that will require immediate intervention.
What is an MRI?
An MRI is a form of imaging that uses a magnetic field and radio waves to generate higher definition images of your body. MRIs are generally better at showing the soft tissues of the body.
MRIs are typically not performed at an initial emergency room visit after an auto accident, unless there are indications of a life-threatening issue that cannot be captured in a CT scan of the head. MRI scans can capture a clearer picture of the soft tissues of the brain. This makes it easier to show lesions, microhemorrhages, and other significant tissue damage.
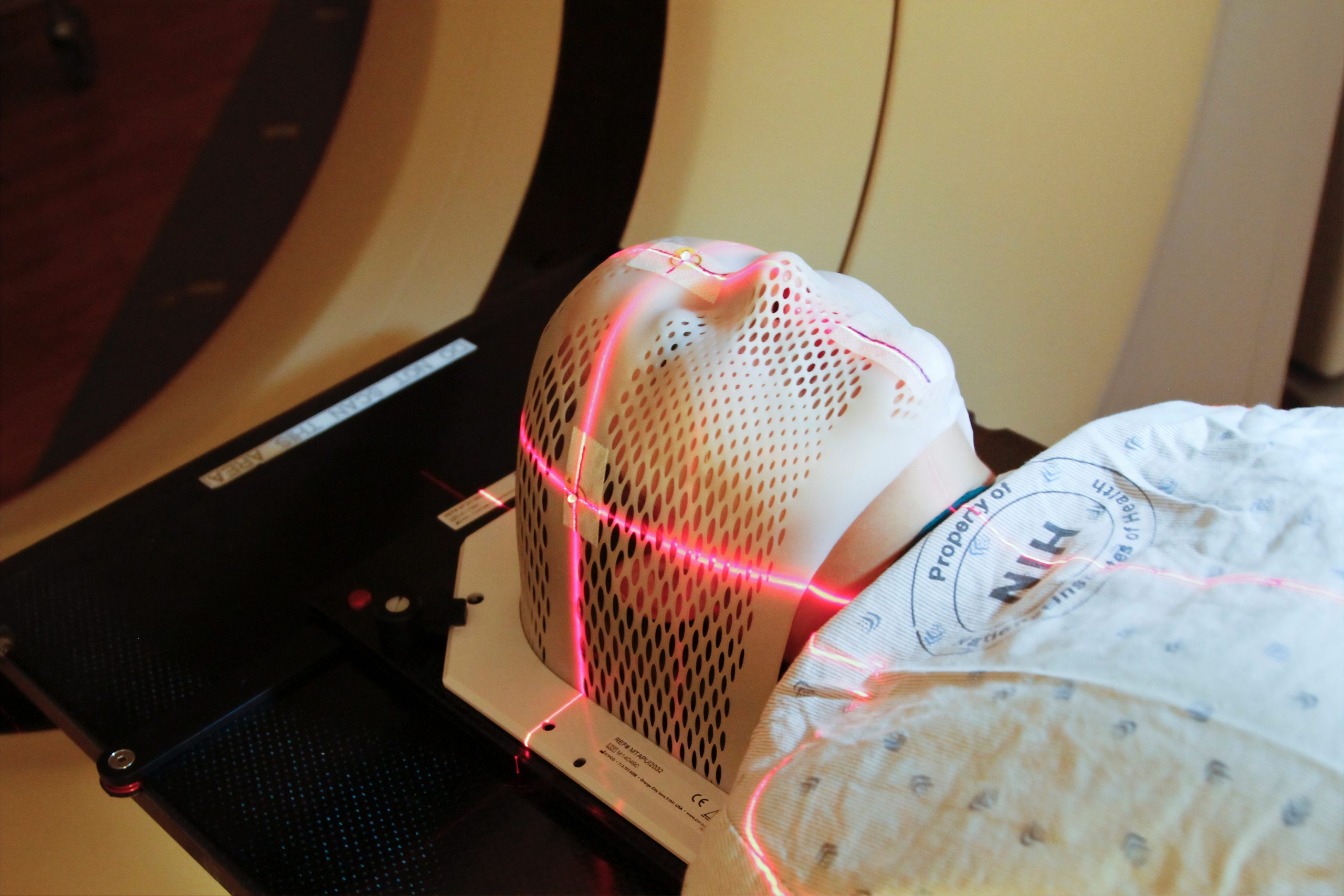

Why can’t an MRI or CT scan reveal my brain injury?
Both forms of imaging were developed for commercial use in the 1970s, and they are only reliable in showing severe traumatic brain injuries. Mild traumatic brain injuries, which make up 80% of all traumatic brain injuries, do not typically damage the brain or skull on a scale large enough for MRIs or CT scans to detect.
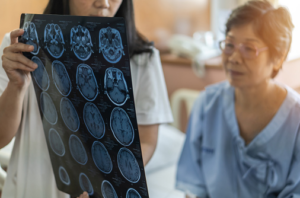
Why communication with your doctor is important
Mild TBIs (mTBIs) can be caused by either a direct blow to the head or a rapid acceleration/deceleration of the skull. That direct blow or shearing effect of the brain moving around in the skull may cause damage to the brain on the cellular level, but can be too small for standard hospital imaging to detect.
This is why it is important to communicate your symptoms to your medical providers, so they can clinically determine whether you have suffered a mild TBI and direct you to the appropriate specialized medical care.
If you have suffered a concussion or traumatic brain injury through no fault of your own, the experienced attorneys at Allen & Allen can help you determine whether you are entitled to compensation. Call today for a free consultation at 866-962-3527.




