We live in a fast-paced world. Whether it’s working overtime, staying up late to finish a project, or socializing with friends, studies suggest that long days and restless nights are common for most of us.
The National Sleep Foundation (NSF) estimates that millions of Americans suffer from “self-imposed sleep deprivation.” Everyone knows that sleep-deprived drivers create serious and potentially deadly car crashes on America’s roadways. A lesser-known fact is that fatigued driving has reached almost epidemic proportions in today’s society.
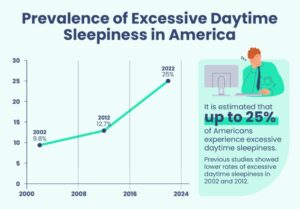
What is fatigued driving considered?
Fatigued driving, also known as drowsy or tired driving, is operating a motor vehicle while feeling sleepy or fatigued. This dangerous behavior is a significant traffic safety concern in the United States.
According to the National Sleep Foundation, drowsy driving is a form of impaired driving, much like drunk driving, and can lead to severe consequences, including accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
Factors contributing to drowsy driving include lack of sleep, long hours behind the wheel, and distractions. The risks associated with drowsy driving are substantial, making it crucial for drivers to recognize the signs of fatigue and take appropriate measures to stay safe on the road.
Fatigued driving risks
Drowsy driving poses a significant risk to everyone on the road, including drivers, passengers, pedestrians, and cyclists. The dangers of driving while fatigued are comparable to those of driving under the influence of alcohol.
Fatigue drivers experience impaired cognitive and motor skills, slower reaction times, decreased attention, and reduced coordination. These impairments increase the likelihood of accidents, injuries, and fatalities.
Who is most at risk?
While this type of driving can affect anyone, certain groups are more vulnerable to this dangerous behavior.
- Young drivers, like those under 25, are more likely to drive after not getting enough sleep
- Shift workers, who often have irregular sleep patterns, are also at higher risk.
- Individuals with sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea or insomnia, may struggle to stay alert while driving.
- Drivers who take medications that cause drowsiness or those who drive long distances or for extended periods are more prone to drowsy driving.
Fatigued driving statistics in the U.S.
The AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety (FTS) estimates that fatigue-related crashes cost the U.S. approximately $109 billion annually. It also revealed the following:
- 36% of Americans drive drowsy or have fallen asleep behind the wheel.
- A Virginia Tech Transportation Institute study shows that fatigue is a cause of 20% of motor vehicle crashes.
- The U.S. Department of Transportation Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCA) estimates that 13% of commercial motor vehicle drivers were considered to have been fatigued at the time of the crash.
- The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration suggests that sleep deprivation causes roughly 100,000 police-reported accidents, 71,000 injuries, and 1,550 fatalities every year.
How does sleep deprivation affect driving?
Sleep deprivation impairs performance and alertness, and results in memory and cognitive impairment, all of which impact the ability to drive safely. Similar to distracted driving, sleep deprivation impairs performance and alertness, leading to dangerous driving conditions.
Sleep research shows startling similarities between the performance of people who are fatigued and those who are intoxicated. Someone who has been awake for 24 hours performs at the same level as someone who has a .10 percent blood alcohol level, which is high enough to qualify as a drunk driver in all 50 states.

How has sleep deprivation affected the trucking industry?
Though trucking companies have regulations in place for their drivers, the industry is notorious for incentivizing its workers to drive faster, longer distances, and with even more cargo. This issue has led to unhealthy practices, such as driving while sleep-deprived, falsifying logs, and the use of stimulants to continue their route. And when truck accidents do happen, they can be tragic.
In Chippewa Falls, a 23-year-old tractor-trailer driver fell asleep behind the wheel, causing him to enter a ditch and eventually roll his truck onto a westbound highway lane. Minutes later, a charter bus carrying a school band crashed into the truck, killing five and injuring 29 others.
The truck driver was charged with five counts of homicide by negligent operation of a vehicle and 29 counts of reckless driving that caused great bodily harm. He had falsified his logs to say he was sleeping at the time.
Thankfully, the FMCSA has promoted regulations restricting commercial drivers from driving more than fourteen hours straight. Regulations such as this “14 hour rule,” help to ensure that tractor-trailer drivers are alert and fit to drive before they get behind the wheel.
Failure to abide by this regulation subjects truck drivers to negligence claims and opens up the possibility for punitive damage awards in civil cases.
Sleep statistics and the trucking industry
- Many studies conducted on the sleeping and driving habits of commercial truck drivers concluded that an unhealthy lifestyle (sedentary work, fast food) long working hours, and sleeping problems were the main causes of drivers falling asleep while driving.
- In a recent study, 17% of commercial drivers were reported as having “over-the-counter drug use” at the time of a crash.
- Three out of every four commercial drivers report having experienced at least one type of driving error as a result of drowsiness.
What to know about medication and drowsy driving
Certain medications can significantly increase the risk of driver fatigue. Common culprits include tranquilizers, sleeping pills, allergy medicines, and cold medications.
These drugs often come with warning labels advising against operating vehicles or machinery while under their influence. Drivers must read these labels carefully and avoid driving if the medication may cause drowsiness. Being aware of the potential side effects of medications can help prevent drowsy driving incidents.
Tips to avoid being sleep deprived while driving:
Make adequate sleep a priority:
Be sure to get an adequate amount of sleep each night. If possible, do not drive while your body is naturally drowsy. According to the average circadian rhythm, this is between 12 a.m. to 6 a.m., and 2 p.m. to 4 p.m.
The circadian rhythm refers to the wake/sleep cycle that our body goes through daily. The cycle involves our internal clock and controls our daily pattern of alertness.
With inadequate sleep, the drowsiness experienced during natural “lulls” can be even stronger and may have a greater adverse effect on a driver’s performance. If you do become drowsy while driving, be sure to choose a safe place to pull over and rest.
Maintain a healthy diet:
Skipping meals or eating at irregular times may lead to fatigue and/or food cravings. Also, going to bed with an empty stomach or immediately after a heavy meal can interfere with sleep. A light snack before bed may help you achieve more restful sleep.
Take a nap:
If possible, you should take a nap when feeling drowsy or less alert. Naps should last a minimum of 10 minutes, but ideally should last up to 45 minutes.
Allow at least 15 minutes after waking to fully recover before driving. Little-known fact: Short naps are more effective at restoring energy levels than coffee.
Avoid medication that may induce drowsiness:
Most drowsiness-inducing medications include a warning label indicating that you should not operate vehicles or machinery while under the influence.
Some of the most common medicines that may make you drowsy are tranquilizers, sleeping pills, allergy medicines, and cold medications.
Recognize the signals and dangers of drowsiness:
Indicators of drowsiness include frequent yawning, heavy eyes, and blurred vision.
Do not rely on tricks to keep you awake:
Behaviors such as smoking, turning up the radio, drinking coffee, opening the window, and other gimmicks are not real cures for drowsiness and may give you a false sense of security. Excessive intake of caffeine can also cause insomnia, headaches, irritability, and nervousness.
Plus, it takes several minutes for caffeine to get into your system and deliver the energy boost you need, so if you are already tired when you first drink a caffeinated drink, it may not take effect as quickly as you might expect. In addition, if you are a regular caffeine user, the effect may be much smaller.
Why personal injury attorneys are important for your case
If you or a loved one have been injured by a fatigued driver, you need to know that proving sleep deprivation can be difficult.
While a blood alcohol test will show whether a driver was drunk, skid marks can be used to establish that a driver was speeding, and phone records will reveal if a distracted driver was texting or making a call before an automobile accident, sleep deprivation is a state of mind that leaves no permanent record behind.
When a sleep-deprived driver causes an accident, thorough and diligent investigation is essential. Instead of criminal penalties, civil suits for negligence and the possibility of a punitive damage award may be an injured person’s only avenue to justice.
If you have been injured in an accident through no fault of your own, get in touch with the experienced personal injury lawyers at Allen & Allen by calling 866-388-1307 today.




